Model NO.: pH Sensor
Communication method: RS485(Modbus RTU)
Measurement range: 0~14PH
Measurement precision: ±0.1PH
Measurement principle: Glass Electrode Method
Voltage: DC12V~DC24V
Protection class: IP68


Model NO.: pH Sensor
Communication method: RS485(Modbus RTU)
Measurement range: 0~14PH
Measurement precision: ±0.1PH
Measurement principle: Glass Electrode Method
Voltage: DC12V~DC24V
Protection class: IP68
The pH Sensor is a high-precision digital industrial sensor featuring an RS485 communication interface with a standard Modbus protocol, allowing seamless integration with various control and monitoring systems.
It is designed with a corrosion-resistant housing and an IP68 protection rating, ensuring reliable performance in harsh and continuously submerged environments.
The sensor uses an industrial-grade combination electrode with a double-junction reference design, providing long service life and excellent chemical resistance.
It is also equipped with a built-in PT1000 temperature sensor and an automatic temperature compensation algorithm, achieving an accuracy of ±0.1°C for precise and stable pH measurement.
2. Operation Principle
The glass electrode method for measuring the pH of water samples uses a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as the reference electrode and a glass electrode as the indicator
The glass electrode method is used to measure the pH value of water samples.
A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) acts as the reference electrode, while a glass electrode serves as the measuring electrode. Together, they form an electrochemical cell with the sample solution.
The electromotive force (EMF) generated by this cell is detected by the pH meter and converted into a pH reading.
This method offers high accuracy, fast response, and strong resistance to interference from color, turbidity, colloidal substances, oxidants, reductants, and salinity—making it ideal for diverse industrial and environmental water testing applications.
Before powering the device, always verify wiring polarity and sequence to prevent damage from incorrect connections.
Since the cables may be immersed in water (including seawater) or exposed to air for long durations, they must possess corrosion-resistant properties.
All connection points must be properly waterproof-sealed to ensure long-term measurement stability and safety.
4. Maintenance and Servicing
4.1 Usage and Maintenance
When using a pH sensor for measurement, it should first be thoroughly cleaned in distilled water (or deionized water), then blotted dry with filter paper to prevent impurities from being introduced into the solution being measured. ⅓ of the sensor should be inserted into the solution during measurement.
When the sensor is not in use, it should be cleaned and inserted into a container filled with a 3.5 mol/L potassium chloride (KCl) solution.
Check whether the terminals are dry. If contaminated, clean them with anhydrous alcohol and dry thoroughly before use. Avoid prolonged immersion in distilled water or protein solutions, and prevent contact with silicone-based oils. For sensors with extended use, if the glass membrane becomes translucent or accumulates deposits, wash with dilute hydrochloric acid followed by water rinsing. When measurement errors occur due to prolonged sensor usage, calibrate with the corresponding instrument.If calibration and measurement remain impossible after performing the above maintenance and care procedures, this indicates that the sensor has failed and should be replaced.
pH Reference Table for Standard Buffer Solutions
|
Temp(℃) |
4.00 |
4.01 |
6.86 |
7.00 |
9.18 |
10.01 |
|
0 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
6.98 |
7.12 |
9.46 |
10.32 |
|
5 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
6.95 |
7.09 |
9.39 |
10.25 |
|
10 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
6.92 |
7.06 |
9.33 |
10.18 |
|
15 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
6.90 |
7.04 |
9.28 |
10.12 |
|
20 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
6.88 |
7.02 |
9.23 |
10.06 |
|
25 |
4.00 |
4.01 |
6.86 |
7.00 |
9.18 |
10.01 |
|
30 |
4.01 |
4.02 |
6.85 |
6.99 |
9.14 |
9.97 |
|
35 |
4.02 |
4.02 |
6.84 |
6.98 |
9.17 |
9.93 |
|
40 |
4.03 |
4.04 |
6.84 |
6.97 |
9.07 |
9.89 |
|
45 |
4.04 |
4.05 |
6.83 |
6.97 |
9.04 |
9.86 |
|
50 |
4.06 |
4.06 |
6.83 |
6.97 |
9.02 |
9.83 |
5. Sensor Calibration
a) Zero Point Calibration
1. Measure 250 mL of distilled water and pour it into a beaker.b) Slope Calibration
For Acidic Solution:
1. Measure 250 mL of distilled water and add pH 4.00 calibration powder.For Alkaline Solution:
1. Measure 250 mL of distilled water and add pH 9.18 calibration powder.
1. Signal Output: RS-485 (Modbus/RTU protocol). Facilitates seamless integration with third-party devices such as PLC, DCS, industrial PC, universal controllers, paperless recorders, or touchscreen;
2. Dual high-impedance differential amplifier, offering strong anti-interference capability and high-speed response;
3. The company holds a patented pH electrode technology, where the internal reference solution permeates extremely slowly through the microporous salt bridge under a pressure of at least 100 kPa (1 bar), with continuous efflux sustained for over 20 months.
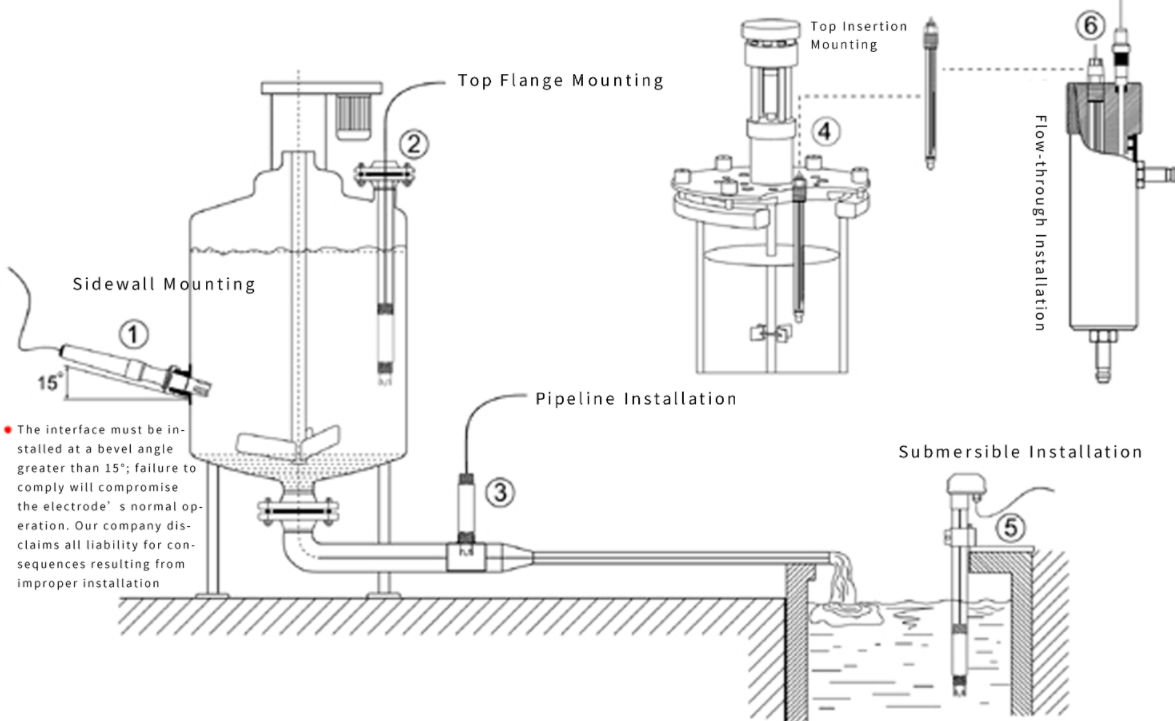
4. Easy Installation: 3/4 NPT (National Pipe Thread) pipe threads enable submersible mounting or integration into pipelines and tanks;
5. IP68 protection class;