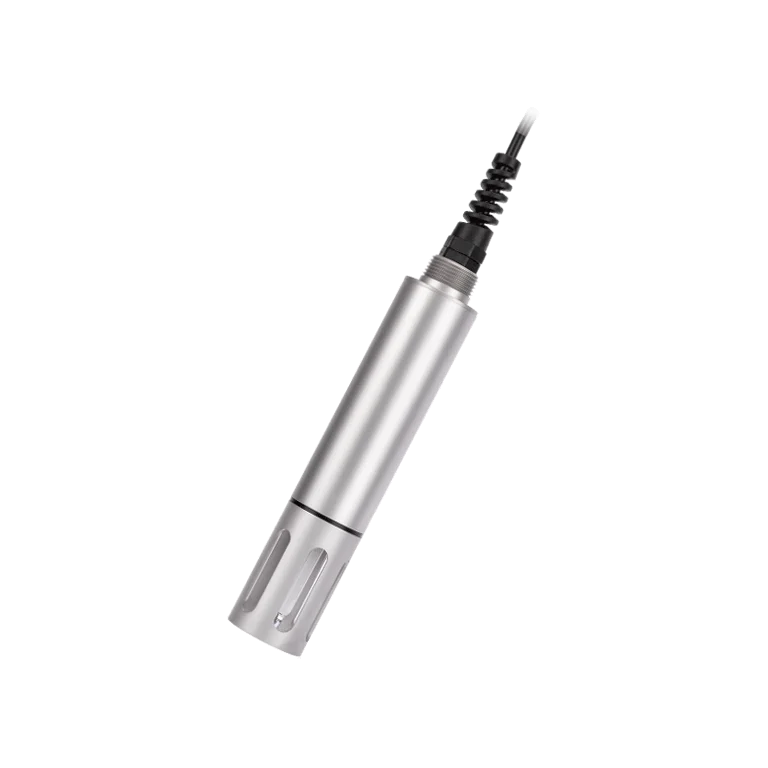
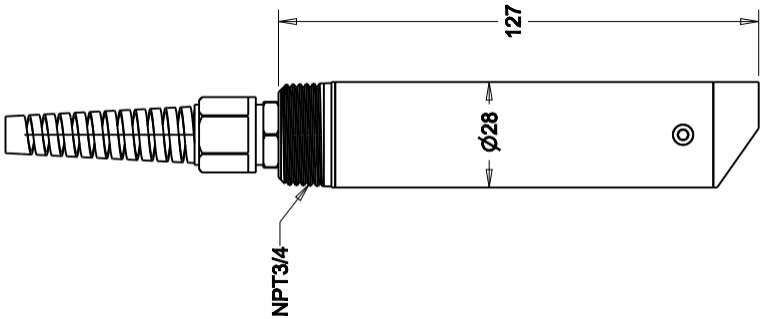
1. Product Introduction
The Turbidity Sensor is an intelligent online water quality monitoring instrument consisting of a control unit and a turbidity sensing probe.
The sensor utilizes RS485 communication with the Modbus protocol, offering strong anti-interference capability and stable data transmission.
The control unit supports multiple output interfaces—including analog, digital, and relay signals—to seamlessly integrate with existing monitoring systems and data platforms.
Engineered for long-term field operation, this infrared turbidity sensor provides high measurement accuracy, fast response, and excellent stability, making it suitable for industrial wastewater, surface water, and municipal applications.
2. Measurement principle
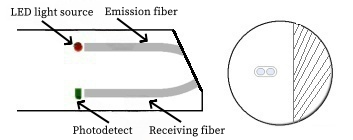
The turbidity sensor operates in full compliance with the ISO7027 international standard.
It employs an infrared LED light source that emits radiation through an optical emission fiber, illuminating suspended particles in the water sample.
These particles cause light scattering, and the scattered light intensity—collected at a 90° angle via a receiving optical fiber—is detected by a high-sensitivity photodiode.
Through photoelectric conversion, signal conditioning, and algorithmic compensation, the system calculates the turbidity value of the sample.
This infrared scattering method ensures accurate and stable measurement results, even under varying color, salinity, or transparency conditions.
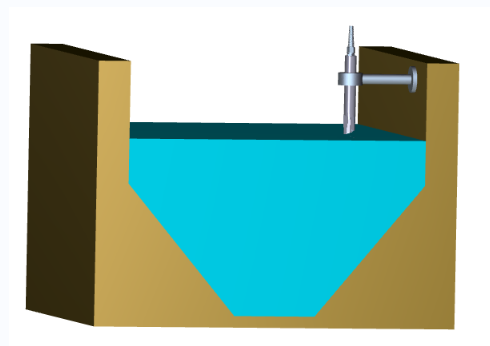
3. Application
The Turbidity Sensor is widely used in environmental protection, industrial process control, and water resource management, including:
• Wastewater treatment: Continuous turbidity monitoring in sewage and industrial effluent discharge outlets.
• Drinking water systems: Real-time monitoring of turbidity in water intake, purification, and distribution processes.
• Environmental monitoring: Long-term observation of surface water and groundwater quality changes.
4. Routine maintenance
To ensure consistent accuracy and extend sensor lifespan, routine maintenance should include:
• Cable Inspection: Regularly check signal and power cables for damage, aging, or water ingress.
• Visual Inspection: Examine the main unit and sensor housing for physical damage, corrosion, or fouling.
• Cleaning: Periodically clean the optical windows and sensor body using a soft cloth or brush to remove biological deposits or sediment buildup.